Latent Heat Is Best Described as
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a body. What is Sensible Heat.
Ammonia aqueous solutions are often labeled as ammonium hydroxide but are actually best described as ammonia molecules dissolved in water with only a few percent being converted to ammonium and hydroxide ions.
. L is the specific latent heat. That associated with vaporizing a liquid or a solid or condensing a vapour is called the heat of vaporization. What I would do in your place is to employ a.
In studies of the heat budget of the global free atmosphere the concept of latent heat now known as enthalpy of condensation plays an important role 1. The heat absorbed or released per unit mass when water changes phase D. The following tables show the weekly forecasts for several days during the summer and winter in Greenville Mississippi.
The pathogenic factor goes into the Interior it changes into. 334 kJ of energy. The horizontal transport of energy in the atmosphere.
A substance has a melting point of 20C and a heat of fusion of 36 104 Jkg. Latent heat also known as latent energy or heat of transformation is energy released or absorbed by a body or a thermodynamic system during a constant-temperature process usually a first-order phase transition. Latent heat of vaporization is what causes that heat to be released.
A substance has a melting point of 20C and a heat of fusion of 36 104 Jkg. The heat absorbed or released per unit mass when water changes phase O C. M is the mass of a substance.
The best SHS liquid available is Water be-cause it is cheap and has a high specific heat. The latent heat is a hidden energy of the system and does not affect the temperature of a substance - for example water remains at 100C while. Latent heat is the work done in a system in order to hold the atoms or molecules of matter in the same phase.
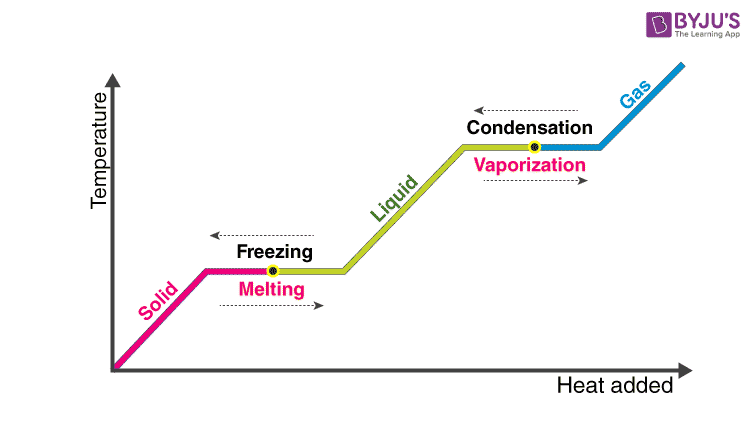
Which of the following best describes latent heat. The latent heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid is called the heat of fusion. The heat transfer from molecule to molecule both of which must be touching O B.
Therefore this term describes the change of phase regarding the internal energy of the system. At 0C liquid water has 334 J g1 more energy than ice at the same temperature. The latent heat is normally expressed as the amount of heat in units of joules or calories per mole or unit mass of the substance undergoing a change of state.
The specific heats for the solid liquid and gaseous phases are 600 Jkg K solid 1000 Jkg K liquid and 400 Jkg K gaseous. The heat Q required to change the phase of a sample of mass m is given by. Sensible heat affects dry-bulb temperature whereas latent heat affects moisture content.
The annual purchased energy saved by a passive heating system compared to a building heated by a conventional heating system The primary difference between sensible and latent heat is. Specific latent heat is characterized as the measure of heat energy heat Q that is consumed or discharged when a body experiences a steady temperature process. Latent Heat in Chinese Medicine.
The boiling point is 150C and the heat of vaporization is 72 104 Jkg at a pressure of one atmosphere. Latent heat is a form of internal or potential energy stored by evaporated or melted water. Latent Heat or Latent Pathogenic Factor is a pathology that is quite unique and rather difficult to comprehend.
Latent heat is defined for a system with constant temperature. Question 13 Which of the following best describes latent heat. A net transfer of heat upward away from the surface O D.
Heat released or absorbed when a substance changes state without a change in temperature. A total of 334 J of energy are required to melt 1 g of ice at 0C which is called the latent heat of melting. What is Latent Heat of Fusion.
The rock bed type storage materials are used for air heating appli-cations 2. A net transfer of heat upward away from the surface O C. However above 100 C oils molten salts and liquid metals etc.
The boiling point is 150C and the heat of vaporization is 72 104 Jkg at a pressure of one atmosphere. Melting and freezing point Throughout history melting points have been used to define the temperature at which solids become liquids. 1 klimatos 411 36 1.
Dont use latent heat of H2O and NH3 - it will give you wrong conclusions. The quantity of heat which is absorbed or released by a substance during a change of state fusion or vaporization at constant temperature. The heat transfer from molecule to molecule both of which must be touching B.
The specific heats for the solid liquid and gaseous phases are 600 Jkg K solid 1000 Jkg K liquid and 400 Jkg K gaseous. 232 Latent Heat Storage. Both observation and experiment confirm that when humid air condenses the temperature of the remaining air increases 2.
Is Melting release or absorb energy. Latent heat of fusion also known as enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy that must be supplied to a solid substance typically in the form of heat in order to trigger a change in its physical state and convert it into a liquid when the pressure of the environment is kept constant. The formula for specific latent heat is.
Q is the heat retained or discharged. All energy released during melting is converted to the latent heat of fusion which maintains a constant temperature. Forecast During a Week in the Summer High Temperature F Low Temperature F Average Humidity.
Essentially Latent Heat is formed when an exterior pathogenic factor invades the body without causing symptoms at the acute stage. Fog is best described as A. - known as latent heat since it doesnt show up as a change in temp - when heat is changing during the same phase of matter the temp will change and kinetic energy increases latent heat graph latent heat of fusion -temp remains constant as solid changes to liquid -used for melting or freezing latent heat of vaporization.
Q mLf Q mL f melting or freezing Q mLv Q mL v evaporating or condensing where the latent heat of fusion Lf and latent heat of vaporization Lv are material constants that are determined experimentally. A Energy is required to partially. During the summer in Maine fog sometimes forms.
The horizontal transport of energy in the atmosphere Movina teanntha.

Latent Heat Definition Types Formula Fusion And Vaporization

Sensible Heat Vs Latent Heat And Temperature Control During The Phase Download Scientific Diagram


0 Response to "Latent Heat Is Best Described as"
Post a Comment